FMEA tools are the ones which are used as a risk assessment tools which stands for Failure Modes and Effects Analysis. FMEA tool is a tool which is used for conducting systematic, and proactive analysis of a process or product in which harm may occur. In FMEA analysis, the FMEA team will gather together from various process areas in order to review convenes to predict and record of the future failure modes by answering: where, how, and to what extent the system might fail. FMEA can also be treated as continuous improvement tool to improve business processes of an organization.
FMEA is a risk assessment tool and here is the FMEA meaning, Failure Mode Effects and Analysis. FMEA is a structured approach wherein the risk assessment teams identify all the possible ways in which a product or process can fail, which is known as potential failures. Not only that, but the team also identifies what are the subsequent effects, specify the severity of those potential failures, and assess the likelihood of their occurrences, in order to find out the RPN (risk priority numbers) values of such risks.
FMEA tool stands for failure mode and effects analysis, which is a risk assessment tool for identifying potential failures or problems and their impact. When it comes to customer expectations and customer requirements, the bottom line goes something like this: a product or process must be delivered with zero defects. This is because, for any customer a defect means non-value added work, waste generation, and high cost impact.

We all must remember that when you come across any problem or a defect in any product or service, it’s going to be expensive. You need to spend huge amount of money, time, and resources in order to fix them. Due to high expectations from customer and an increasing competition in the market, for any supplier it has become a prime objective to deliver quality and reliable products and services with first time right principle.
We all know that many faults or defects in products and services are usually detected through extensive testing or predictive maintenance in the later stages of development. But the worst part of finding a problem in these stages is that it will result in delays in delivery schedules, or delays in deliverables which in turn will be adding significant costs to your planning, execution, and deliveries. This will be going to hamper your profits and expenses.
To overcome such issues, the only solution to all the problems is to follow the principle of first-time-right. This is a high-quality project management which will help you ensure the design with quality and reliability at the beginning of the project management phases, such that the defects will never arise in the first place. One such tool is the FMEA tool which will help you overcome and eliminate the problems, potential failures, and risks in your products and services, way before the start of initial sample building or prototyping.
Contents
- 1 What is FMEA?
- 2 Purpose of FMEA Tools
- 3 FMEA Tools: The Basics
- 4 How to find FMEA failure modes? And how FMEA works?
- 5 Criteria for FMEA Analysis
- 6 Setting FMEA Priorities
- 7 Identifying FMEA Corrective Actions
- 8 FMEA Tool Instructions – How to Use FMEA Tools?
- 9 FMEA Tool Examples
- 10 FMEA Tool Template
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is FMEA?
FMEA stands for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. FMEA is a proactive approach known as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), which is used to identify potential failures in business processes or of an organization in order to either prevent them from occurring or reduce their impact by determining where they might occur and how much is going to be their impact.
The methodical approach that FMEA takes to determining and addressing the causes of failures can aid in avoiding costly issues in manufacturing, enhancing product quality and service dependability, and increasing customer satisfaction. FMEA is one of the best risk assessment tools out their in the world of quality tools.
Purpose of FMEA Tools
The main purpose of FMEA tool is to help the teams, to review, evaluate, and record the following:
- FMEA process steps
- Failure Modes (What could go wrong?)
- Failure Causes (Why would the failure happen?)
- Failure Effects (What would be the consequences of each failure?)
- Severity Rankings (How much severe is the failure?)
- Occurrence Rankings (What are the occurrence levels of such failures?)
- Detection Rankings (How much level is the detection of such failures?)
- RPN Values (the Risk priority number = Severity x Occurrence x Detection)
- Recommended Actions (What is the action plan to reduce the Severity, Occurrence, and Detection?)
- Responsibility and Target Dates (Who is responsible for implementation of recommended action and what is the deadline to finish the recommended action implementation?)
The sole purpose of FMEA tool by any organization is to evaluate each of the processes for all the future possible failures in order to prevent them from future failures by proactively working towards corrective actions implementation. The FMEA approach focuses on prevention rather than detection. It further focuses on finding out the potential failures of products and services, take necessary actions, and implement the actions, so that any future surprises or any later design changes and expenses can be prevented.
The FMEA tool emphasizes on prevention of failure modes by identifying risks, reducing, or eliminating the risks in the form of risk priority numbers or high risk to medium risk, or medium risk to low risk, and so on. FMEA is especially useful for evaluating the impact of a proposed change to an existing process and evaluating a new process before it is implemented.
FMEA Tools: The Basics
FMEA tool is a qualitative and systematic risk assessment tool, which is created usually in excel sheets or in an any FMEA software tool that helps to create, manage, maintain, and update the structure of FMEA. Irrespective of what tool you use for FMEA, all tools help you in identifying how a product or process might fail in future, and what could be the effects of failure. FMEA is also designed to find all the possible causes of failures and the likelihood of such failures being detected way before their occurrences.
What is an FMEA tools?
FMEA tool is one of the best tools which helps to analyze all potential problems way too early in the project development cycles, which will help the teams and organizations to take quick actions and mitigate all potential problems, risks, and failures. The FMEA is now being used in almost of all industries and organizations. With the existence of FMEA, now organizations can be able to eliminate all future potential problems and avoid any overhead costs, expenses, and penalties that can arise from customers.
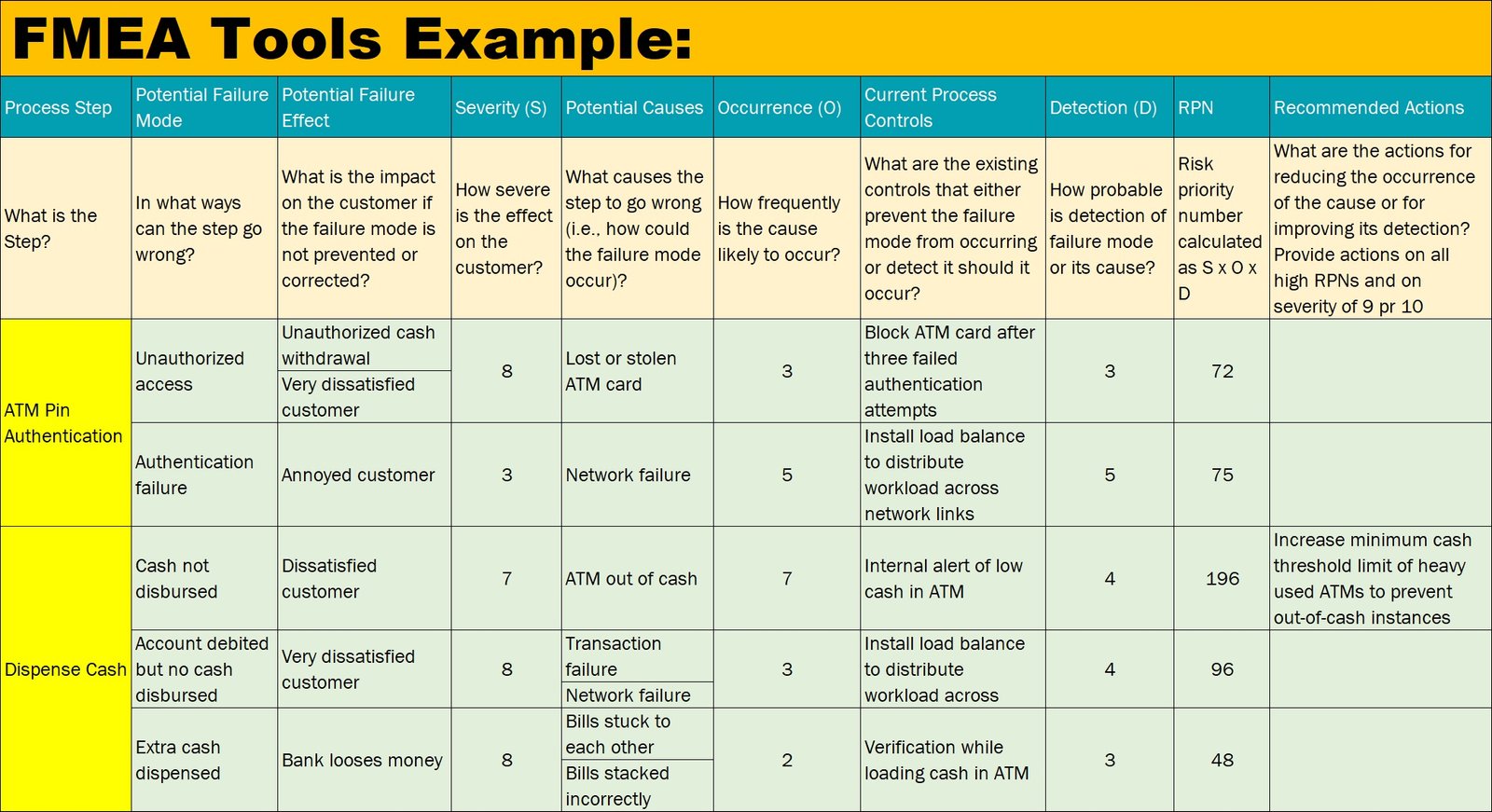
Here is an example of FMEA tool in an excel spreadsheet:
How to find FMEA failure modes? And how FMEA works?
When you want to use any of the FMEA tools, the first step you should be doing is to identify the number of participants. A care should be taken when you are determining the team for FMEA preparation is that the chosen participants must be the process owners from all the concerned key process areas. The participants must be right people who has the right experience.
Among the FMEA participants, few of the process owners who are must are: quality, production, development, design, project management, delivery, and maintenance. These are the people who knows the process better and will help you identify all the real potential failure modes with ease. It is also advised to include the operators or the persons who are really on the job or doing the job for better results and outcomes. The participants team can also be comprising of customers and suppliers as and when needed.
Once you are done with the first step of identifying participants, next step is to start a brainstorming session to find the potential failures and potential causes of the product or service. There is something called as Murphy’s Law which goes something like this: “Anything that can go wrong, will always go wrong”.
So, keeping in mind of this law, all the participants must identify all the components, systems, sub-systems, processes, and functions, which could potentially fail to meet the product or process quality and reliability. Here the primary role of the participants must be focused towards identifying the potential effects of failure along with all possible causes for that failure.
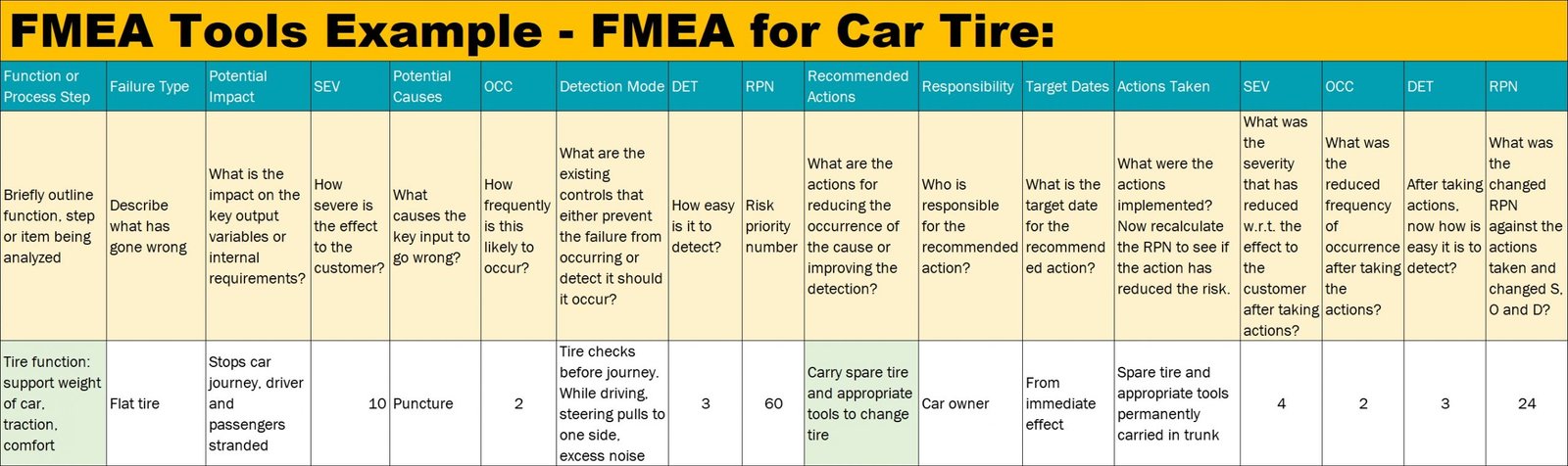
Here is an example of FMEA which can be used as an example when learning how the FMEA works. Here the FMEA team is analyzing the component of a car in order to find out the potential failures along with potential causes. You can go through the Table 1 which talks about the FMEA for Car Tire.
Table 1: FMEA for Car Tire
Criteria for FMEA Analysis
When it comes to FMEA analysis using any of the FMEA tools, basically there are three criteria to assess a problem:
- The severity of the effect on the customer
- How frequently the problem is likely to occur
- How easily the problem can be detected
The FMEA team must assess the problem as per FMEA tools requirements, which allows you to set and agree on a ranking between 1 and 10 (where, 1 being the low ranking, and the 10 being high ranking) for the severity, occurrence, and detection levels for each of the failure modes. While rating, it is always advised to rate by referring to the AIAG FMEA Standard or AIAG-VDA FMEA Standard. The team should quantify the decisions that they are going to make for the ratings based on the FMEA standards.
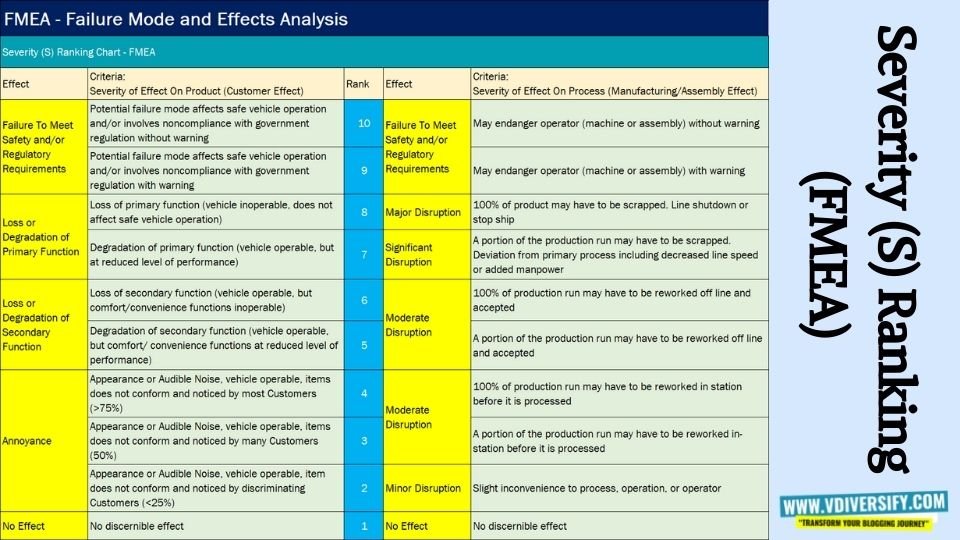
Refer the table below for the Severity Rankings as per AIAG FMEA Standard:
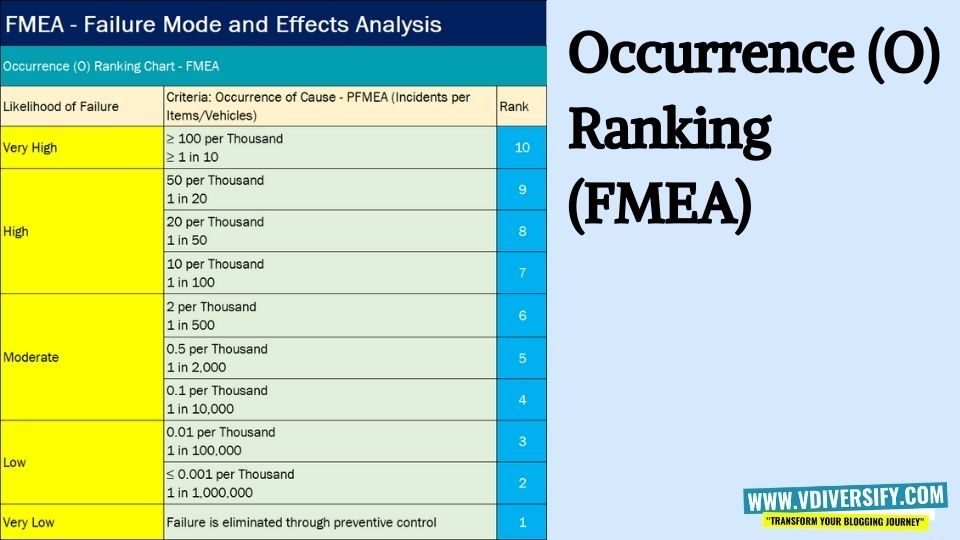
Refer the table below for the Occurrence Rankings as per AIAG FMEA Standard:
Refer the table below for the Detection Rankings as per AIAG FMEA Standard:
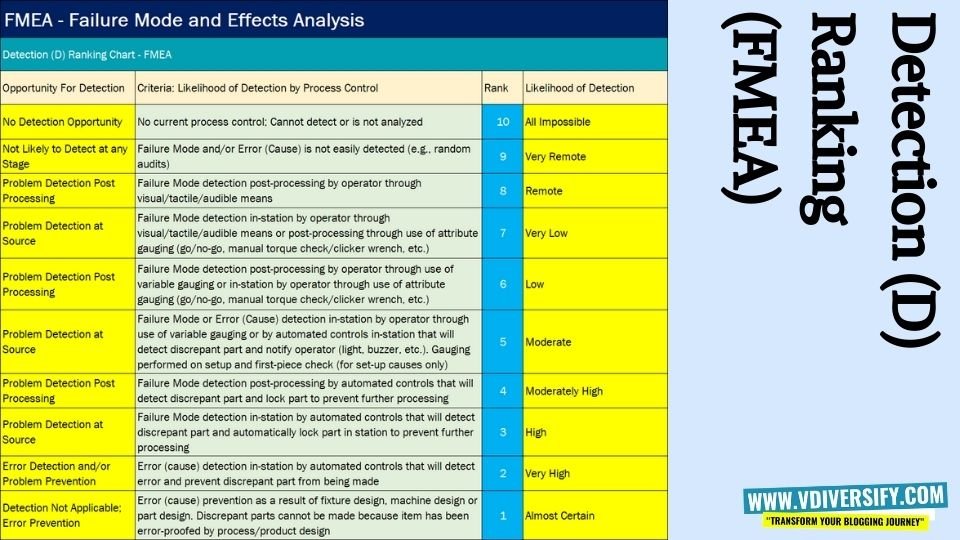
Once the team was able to identify the rankings for severity, occurrence, and detection levels for each of the failure modes identified during the FMEA analysis, now the team can be able to calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN). The formula to calculate RPN goes like this: RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection. For the above example, which we have seen in Table 1, the Severity is rated as 10, the Occurrence is rated as 2, and the Detection was rated as 3. So, the RPN = 10 x 2 x 3 = 60.
Setting FMEA Priorities
Once the team is done with identifying and assessing the FMEA failure modes, now it’s time to adjust the FMEA in order to list all the identified failures in descending order of calculated RPN values. By setting the FMEA with the RPN values in the descending order, you can easily identify the failure modes that needs to pay attention for initiating corrective actions. When resources are limited then, you can choose the ones that have the highest RPN values.
To do so, you can pre-define the threshold RPN value against which you can easily decide on taking the actions that crosses the RPN threshold value. These are the ones that needs highest attention. The RPN threshold value must be defined by considering multiple factors, which includes and are not limited to: quality control, industry standards, and safety requirements, and so on.
However, you can get the best results when you prioritize the starting point by using Pareto Chart or 80:20 rule. This rule means that, the 80 percent of issues are caused by 20 percent of the potential problems. The thumb rule of pareto analysis says that the FMEA teams must first focus on the failures with the top 20 percent of the highest RPN values.
Identifying FMEA Corrective Actions
Now when you have prioritized the potential problems with highest RPN values, now it’s time to focus on deriving the corrective actions in order to reduce the occurrence of failure modes, or to improve upon the detection levels of such failure modes. Based on the corrective actions derived, the FMEA leader can assign the responsibilities in the form of responsible name, department, and target date, so that the actions can be closed on time.
No you have the FMEA ready, it’s time to implement the corrective actions as per the defined target dates. Once the implementation of corrective actions completed, the FMEA team must meet again, in order to determine the effectiveness of corrective actions that have been taken and to reassess the severity, occurrence, and detection for the top failure modes. This will also help in determining whether you need any other corrective actions for effective reduction of RPN values.
FMEA Tool Instructions – How to Use FMEA Tools?
When it comes to using FMEA tools, here are the following instructions one must follow in order to have a successful FMEA:
- Step 1: Select a process to evaluate with FMEA
- Step 2: Form a multidisciplinary team
- Step 3: Prepare the list of all processes
- Step 4: Prepare and update the FMEA tool with the team
- Step 5: Calculate RPN values and use RPN values for improvement plans
Step 1: Select a process to evaluate with FMEA
FMEA evaluation works best for any processes including sub-processes too. The beauty of using FMEA tool is that you can easily conduct risk analysis of all the processes and products, so that you can prevent any of the future failures that may arise with your product or processes.
If your organization has similar products then it is best advised to go for family FMEA. Each of the processes and sub-processes can broken down into multiple process steps and then evaluate the FMEA. When you use FMEA software tools, the process of FMEA evaluation becomes much easier and effective. You can easily navigate to the required processes easily with the help of FMEA software tools.
Step 2: Form a multidisciplinary team
When it comes to forming an FMEA team, it is very important to note that, you must be involving all the key process owners. The reason is that, they are the ones who actually knows what is really happening in the processes. You can also include customers and suppliers as and when applicable in order to conduct FMEA.
You can also include other members into your FMEA discussions who may not have to be part of the team depending on the requirements of discussions. For example, a logistic support supplier who supports for logistic operations of your organization can be included to evaluate the FMEA tool.
Step 3: Prepare the list of all processes
Now you have formed your multidisciplinary team, it’s time to prepare a list of processes that must be evaluated with FMEA tools. Having multiple key stakeholders from multiple areas will help you in identifying all the processes in your organization, and to which you can able to reduce all the future risks. The best tool to identify all the processes is to make use of process flow chart or process flow diagram, which makes it easier for you to identify all the processes in your organization.
Now you have the list of all processes, you can draw down the FMEA tool table as shown below:
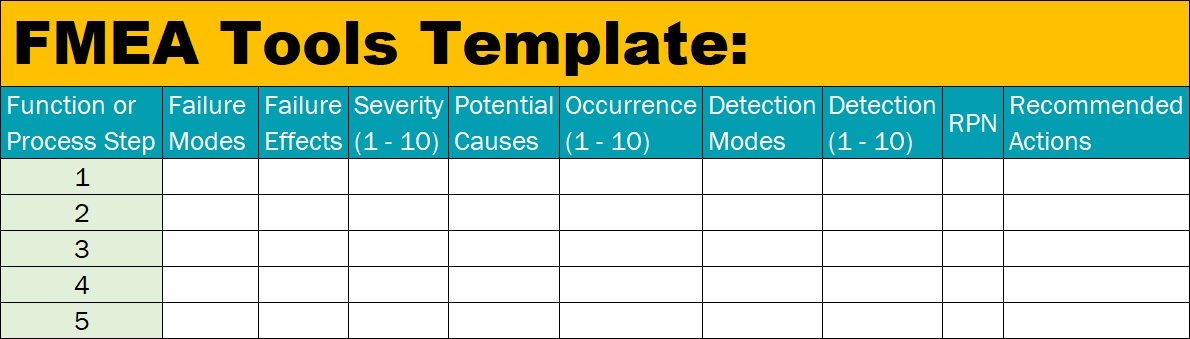
Step 4: Prepare and update the FMEA tool with the team
Now you have the FMEA tool skeleton ready, now its time to update the FMEA tool table in detail for each of the processes. Update all the columns and rows as applicable for each of the processes. Here are the meanings of each cells which will help you get started with FMEA tool usage:
- Failure Modes (What could go wrong?): List out everything that could go wrong during that process step. This step to be followed for each of the process steps.
- Failure Effects (What would be the consequences of the failure?): List out all the possible consequences for each of the possible failure modes identified in the previous columns.
- Severity (1-10): On a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the most likely, what is the likelihood that the failure mode, if it does occur, will cause severe harm?
- Potential Causes (Why would the failure happen?): List all possible causes for each of the failure modes you’ve identified.
- Occurrence (1-10): On a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the most likely, what is the likelihood the failure mode will occur?
- Detection Modes (What are the current and prevention detection levels?): List all the current and prevention detection levels for each of the possible causes identified.
- Detection (1-10): On a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the most likely NOT to be detected, what is the likelihood the failure will NOT be detected if it does occur?
- RPN (Risk Priority Number): For each of the failure modes, identify the RPN values by using the RPN formula, RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection. The lowest RPN possible score will be 1 and the highest score will be 1000.
- Recommended Actions (What are the action plans to eliminate or reduce the risks?): Identify all the possible action plan in order to reduce or eliminate the risk levels of severity, occurrence, detection, and RPN values.
Make a list of possible steps that could be taken to improve safety systems, particularly for failure modes with the highest RPN values. FMEA can be used by teams to evaluate each option. Determine how the RPN would change if various system modifications were made.
Step 5: Calculate RPN values and use RPN values for improvement plans
Now you have the FMEA table ready with all the filled in data, now it’s time to calculate the RPN values. To calculate the RPN values, use the formula, RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection. If there are multiple failure modes for a single process step, then the one with the highest severity must be selected as the severity number in calculating RPN values for each of the failure modes.
Focus must be given towards the failure modes that have the highest RPN values. The ones that have the lowest RPN values should be given less focus, as they are not likely to affect the overall process much, even if they are eliminated completely. The best tool you can use to identify the highest RPN values is to use the pareto analysis or 80:20 rule. Once all the high RPN values are addressed, then you can think of touching down the low RPN values.
Hence, identify the failure modes with the top 10 highest RPN values. These are the ones the team must first consider for improvement actions:
- Use FMEA to plan actions to reduce harm from failure modes
(a) If the failure mode is likely to occur:
- Evaluate the causes and see if any or all of them can be eliminated.
- Consider adding a forcing function (that is, a physical constraint that makes committing an error impossible, such as medical gas outlets that are designed to accept only those gauges that match).
- Add a verification step, such as independent double-checks, bar coding on medications, or alert screens.
- Modify other processes that contribute to causes.
(b) If the failure is unlikely to be detected:
- Identify other events that may occur prior to the failure mode and can serve as “flags” that the failure mode might happen.
- Add a step to the process that intervenes at the earlier event to prevent the failure mode. For example, add pharmacy rounds to remove discontinued medications from patient care units within 1 hour of discontinuation, to decrease the risk that the medications will still be available for use (the failure mode).
- Consider technological alerts such as devices with alarms to alert users when values are approaching unsafe limits.
(c) If the failure is likely to cause severe harm:
- Identify early warning signs that a failure mode has occurred, and train staff to recognize them for early intervention. For example, use drills to train staff by simulating events that lead up to failure, to improve staff ability to recognize these early warnings.
- Provide information and resources, such as reversal agents or antidotes, at points of care for events that may require immediate action.
- Use FMEA to evaluate the potential impact of changes under consideration
FMEA can be used by teams to talk about, analyze, look over, and figure out how each change would affect RPN if it were implemented. Before testing the change in a safe environment, the team can “verbally simulate” it and assess its impact in a secure setting. It is possible for concepts that appear to be great enhancements to actually increase the estimated RPN.
- Use FMEA to monitor and track improvement over time
The process’s total RPN should be calculated by teams, and then a target for improvement should be set. For instance, a group might define an objective of diminishing the complete RPN for the medicine requesting process by half from the standard.
FMEA Tool Examples
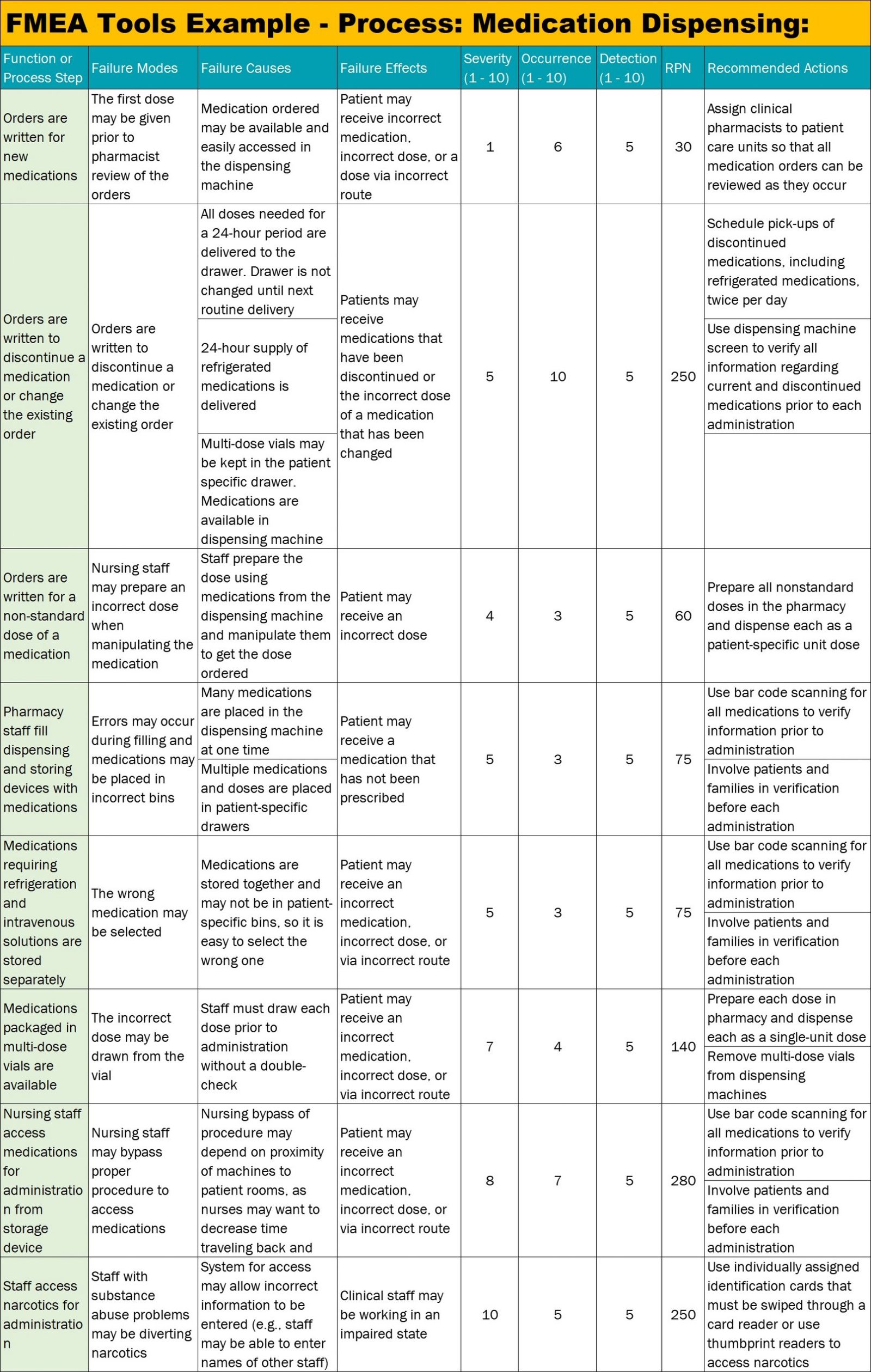
Here is an example of FMEA tool:
Process: Medication Dispensing
FMEA Tool Template
Here is a FMEA tool template:
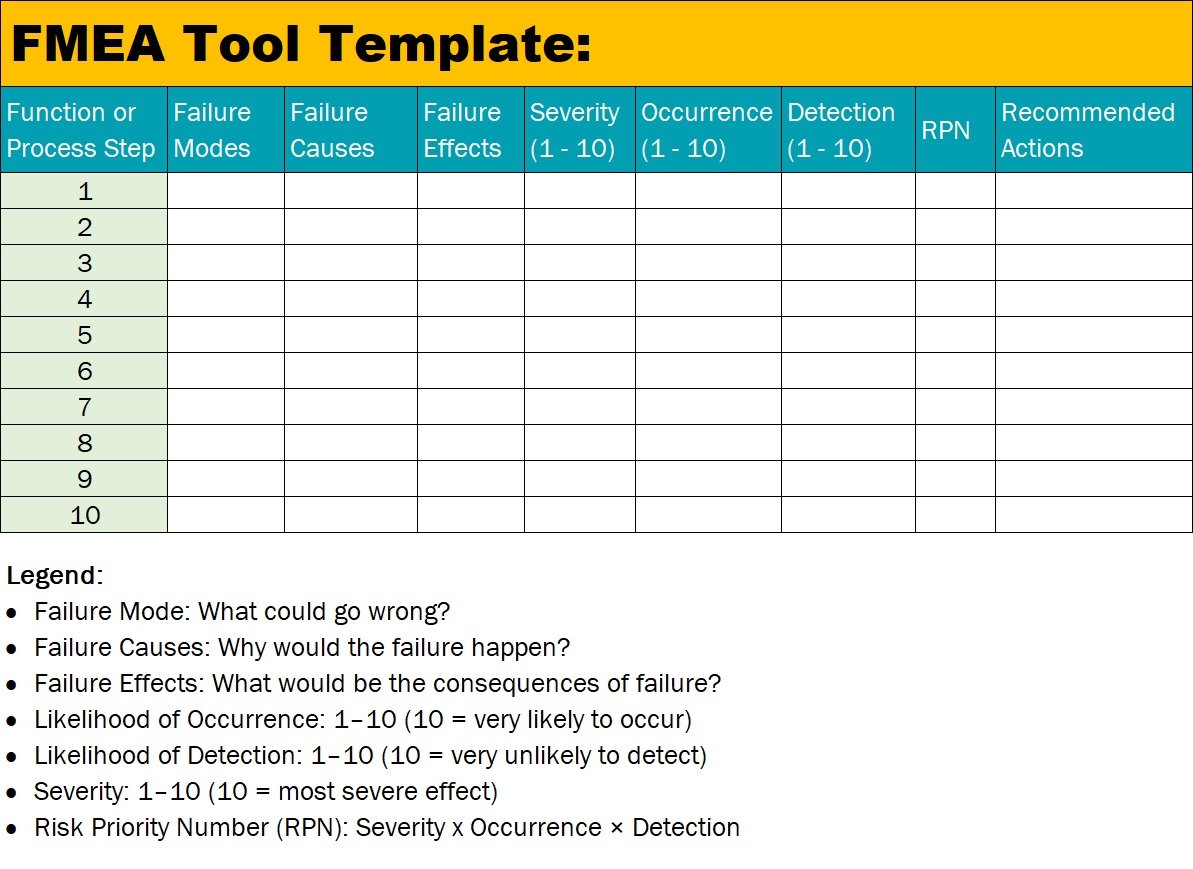
Legend:
- Failure Mode: What could go wrong?
- Failure Causes: Why would the failure happen?
- Failure Effects: What would be the consequences of failure?
- Likelihood of Occurrence: 1–10 (10 = very likely to occur)
- Likelihood of Detection: 1–10 (10 = very unlikely to detect)
- Severity: 1–10 (10 = most severe effect)
- Risk Priority Number (RPN): Severity x Occurrence × Detection
Conclusion
When it comes to risk assessment, the FMEA tools are the one that stands out from the crowd. The FMEA tools is the most valuable risk assessment tool which can be used by multiple organizations for number of benefits.
Some of such benefits include: preventing the potential future defects, preventing the future potential failures of products or services, improving the reliability of products or services, prevention of late costly design changes, avoiding non-value added expenses, increasing product or process quality, and increasing customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is FMEA performed?
FMEA tool is considered as one of the best risk assessment tools. Hence, FMEA is basically used by organizations throughout the product lifecycle to study and reduce the risks in their processes. Usually, the FMEA is performed during the initial design stage or the development stages, which is called as Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (DFMEA). Later the same is carried forward, and Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is performed.
Why FMEA is important?
FMEA is a very important tool when it comes to identifying risks in your products and services so that you can eliminate them during the design stages itself. FMEA is important because, FMEA is a risk assessment tool and is one of the structured way of identifying and addressing potential problems, or failures of future, and resulting effects of failure on the system, product, or processes before any adverse event occurs.
What are the 3 types of FMEA?
Basically when it comes to types of FMEA’s, there are 3 types of FMEA’s and they are: System FMEA, Design FMEA, and Process FMEA. But if you remove System FMEA, then we will be left with 2 types of FMEA’s and they are DFMEA and PFMEA.
Apart from this, there are multiple types of FMEA’s which you can see around many organizations. Each FMEA has its own identity and being different ways. Few of such types of FMEA’s are: Logistics FMEA, Software FMEA, Functional FMEA, and so on.
Is FMEA a Six Sigma tool?
Yes, FMEA is considered by many to be the perfect Six Sigma tool. Since, FMEA is a risk assessment tool, it perfectly fits in the category of Six Sigma tools which basically helps in reducing defects, or eliminating defects, reducing risks, eliminating wastes, and so on. FMEA tool is a highly intuitive tool that helps to overcome, reduce, and eliminate the risks in an organization.
What are the 5 steps of the FMEA process?
Many think that there are only 5 steps in FMEA process, or 7 steps in a FMEA process. In the new AIAG-VDA FMEA, there are basically 7 steps to a process FMEA. However, if you refer the old FMEA standard, then there 10 steps to a Process FMEA and are listed below:
- Step 1: Review the process
- Step 2: Brainstorm potential failure modes
- Step 3: List potential effects of each failure
- Step 4: Assign Severity rankings
- Step 5: Assign Occurrence rankings
- Step 6: Assign Detection rankings
- Step 7: Calculate the RPN
- Step 8: Develop the action plan
- Step 9: Take action
- Step 10: Calculate the resulting RPN
Is FMEA a quality tool?
FMEA is one of the 5 core tools of quality management. FMEA is a high end quality tool that helps to conduct risk assessments in an organization. FMEA is based on the application of a procedure for classifying potential failures based on their severity, frequency and detection capacity. It is the technique par excellence of quality tools. They are the abbreviations of Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA).

“Hey, I am Sachin Ramdurg, the founder of VDiversify.com.
I am an Engineer and Passionate Blogger with a mindset of Entrepreneurship. I have been experienced in Blogging for more than 15+ years and following as a youtuber along with blogging, online business ideas, affiliate marketing, and make money online ideas since 2012.

3 thoughts on “FMEA Tools – What is FMEA? – Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Quick Guide”